Term Structure Strategies
Term Structure Strategies refer to trading strategies that exploit price structure differences between options with the same underlying asset but different expiration dates.
Calendar Spread Strategy
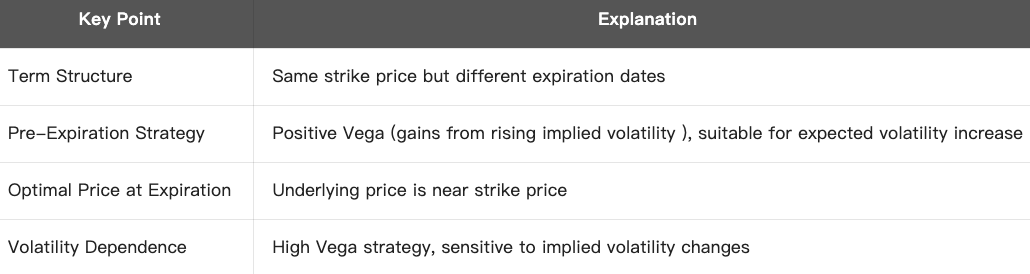
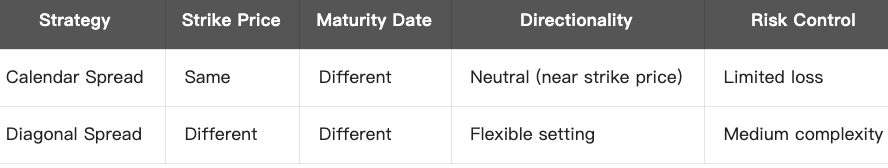
Calendar Spread is an options strategy based on term structure (different expiration dates), also known as Time Spread or Horizontal Spread.
Core Structure: At the same strike price:
- Sell a near-term option
- Buy a long-term option
You can construct a Calendar Spread Strategy using either Calls or Puts.
Example:
Assume that BTC current price is $100,000. You expect little movement in the next few weeks, but anticipate significant volatility afterward.
Then you can create a Calendar Spread Strategy with a BTC $100,000 strike price:
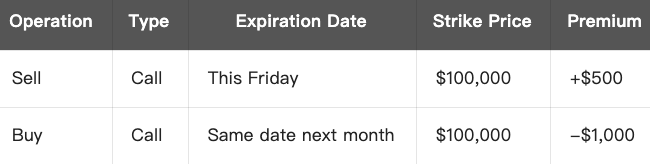
- Total Cost = $1,000 - $500 = Net Expense $500 (max loss)
- At expiration, if BTC is close to $100,000, the near-term option expires while the longer-term option still retains time value, it may lead to a profit from the strategy.
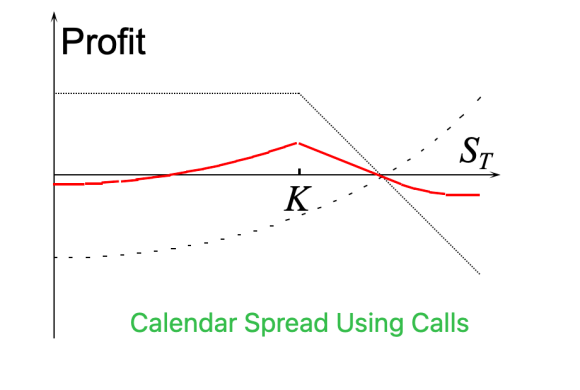
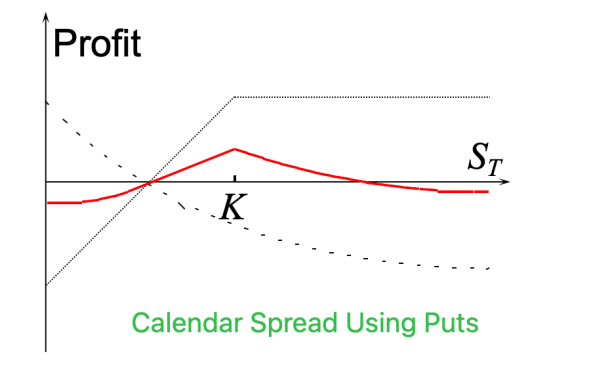
PnL Logic:
- Max Profit: Underlying asset price is near strike price (ATM) when near-term expires.
- Max Loss: Underlying asset price moves far from strike price (Deep ITM or OTM), causing the long-term option to lose value while the near-term option expires worthless.
- Directionality: A neutral-to-volatile strategy, betting on future volatility to increase and current volatility to contract.
- Theta: Selling the near-term option → positive Theta; Buying the long-term option → negative Theta. Theta initially positive then negative.
Strategy Summary:
When to Use?
- The current market shows low volatility but may experience a surge soon (e.g., before major data releases)
- You expect little short-term movement but a potential directional breakout in the medium term.
- Then you can construct a non-directional strategy
Conclusion:
Calendar Spread Strategy profits by buying long-term and selling short-term options with the same strike prices, betting on limited short-term movement but potential significant long-term volatility, making it a classic volatility trading tool.
Diagonal Spread Strategy
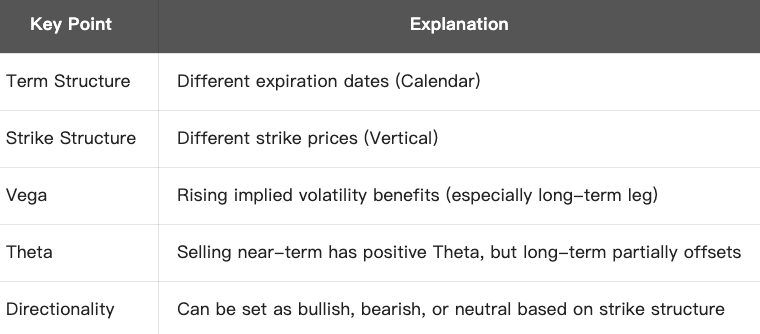
Diagonal Spread is an options strategy combining options with different strike prices and expiration dates. Its name comes from the diagonal pattern.
Core Structure:
- Buy long-term option (more expensive, longer term)
- Sell near-term option (cheaper, expires sooner)
- Use different strike prices
Can be constructed with Calls or Puts.
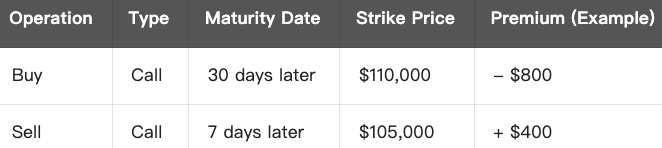
Example (Call Diagonal Spread):
Assume current BTC = $100,000
You expect BTC to rise moderately to around $105,000 next week without violent volatility. You can construct the following strategy:
PnL Logic:
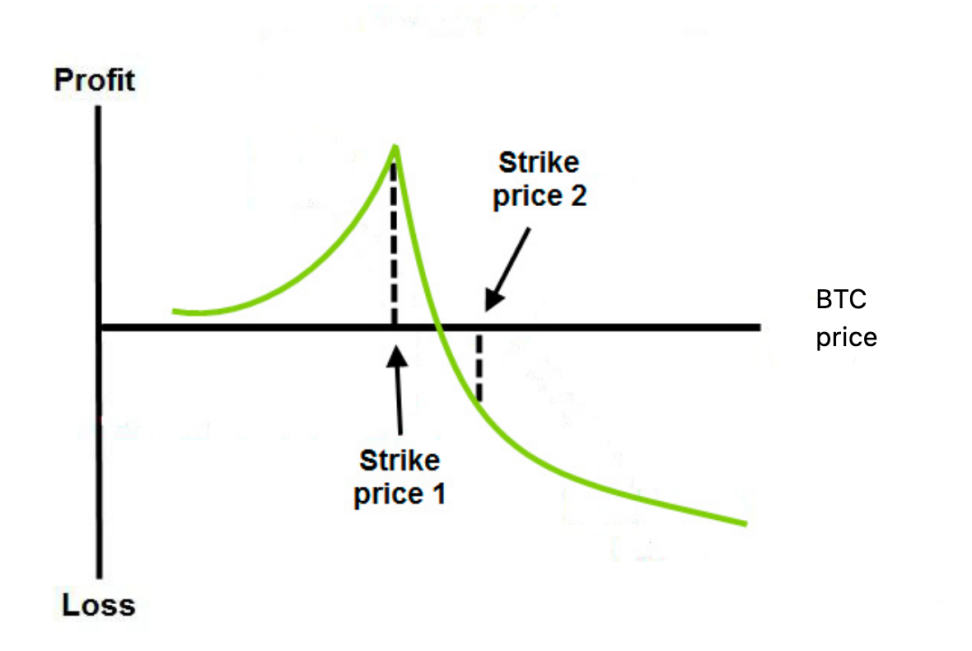
- Profit Zone: BTC near $105,000 when near-term option expires → near-term option’s time value depletes, long-term option retains value
- Max Loss: BTC rallies to break through long-term option’s strike price (e.g., to $115,000+), long-term leg cannot offset Delta loss
- Direction and Timing : Favorable for gradual price increases, unfavorable for sharp spikes (short leg gets assigned)
Strategy Summary:
Diagonal vs Other Strategies:
Application Scenario:
- You’re slightly bullish/bearish but don’t want excessive risk
- You aim to profit from the time decay of the short-term leg while keeping the long-term leg to capture volatility.
- You expect implied volatility to rise (positive Vega exposure)
Conclusion:
Diagonal Spread strategy combines options with different strike prices and expiration dates, allowing fine-tune exposure to direction, volatility, and time decay. It’s suitable for flexible, neutral to mildly directional, short- to mid-term volatility views.





